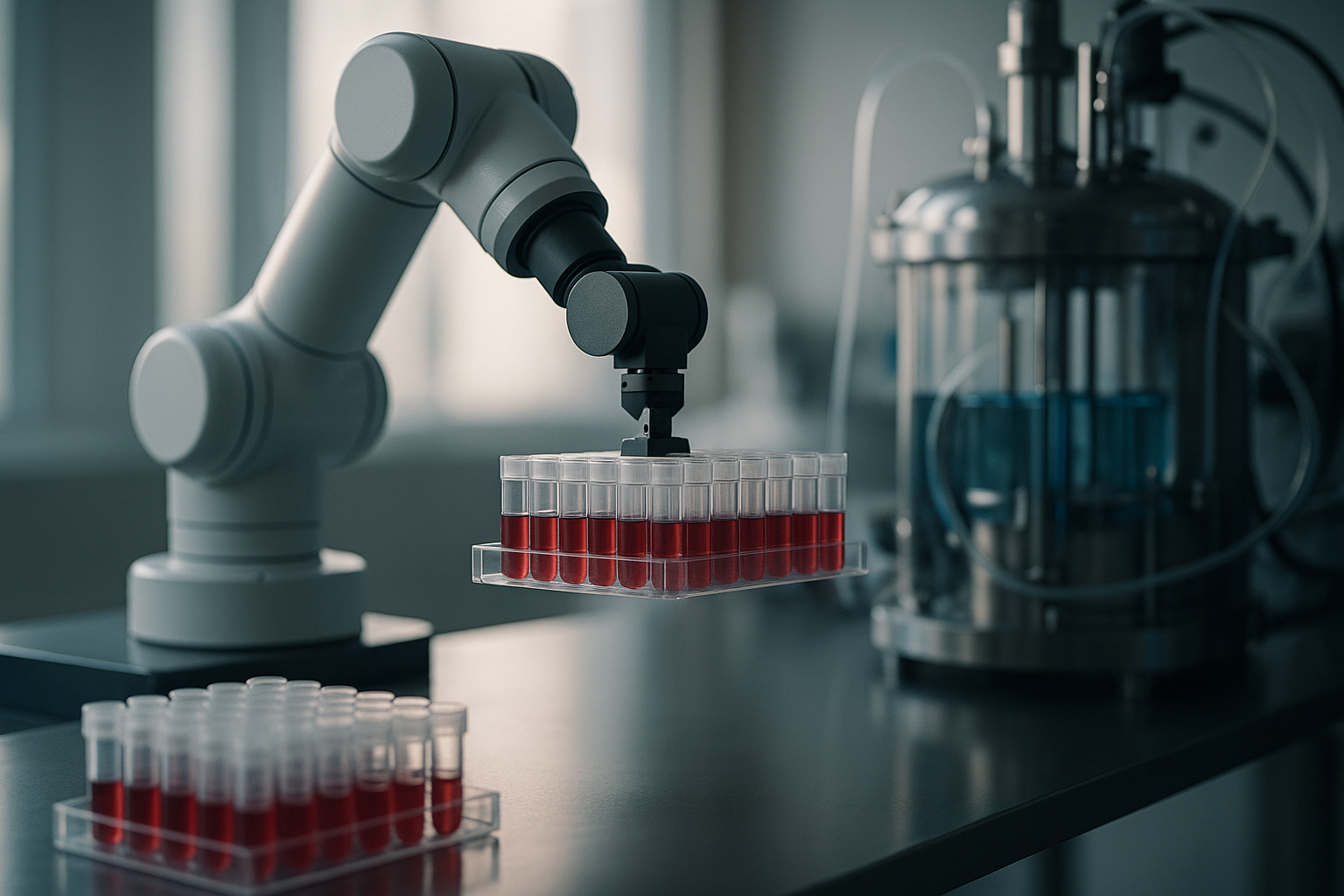
AI’s Next Revolution: Robotic Cell Therapy Manufacturing Moves From Pilot to Production
Biomanufacturers racing to scale advanced therapies face a hard ceiling: high per‑dose costs, scarce cleanroom space, and contamination risk. Multiply Labs’ approach—dense, modular robotics that automate critical steps like T cell expansion—aims to shift that math. In peer‑reviewed work and partner reports, the company demonstrates quality parity with manual processes and substantial economic gains, positioning robotic cell therapy manufacturing as a near‑term catalyst for access and affordability [1][2][3].
What Multiply Labs’ robotic clusters do
Multiply Labs’ modular “clusters” are built for parallelization and compact deployment. Multiple collaborative robot arms—sourced notably from Universal Robots—run tasks simultaneously, with collision avoidance and ceiling‑mounted configurations that maximize vertical space [2]. Crucially, the system is designed to work with leading cell therapy instruments and established protocols, minimizing process redesign and easing adoption in existing GMP facilities [1]. These engineering choices enable dense, floor‑to‑ceiling utilization and streamlined integration with current workflows [1][2].
Peer‑reviewed evidence on automated T cell expansion
A peer‑reviewed study on Multiply Labs’ robotic system reports that automated T cell expansion achieved statistical equivalence to manual processing across critical quality parameters, including cell growth and product characteristics [1]. The data address a core validation hurdle for manufacturers evaluating automated T cell expansion. The study also underscores a key quality and safety benefit: by removing direct human contact with cells, the system maintained sterility—even when operated in non‑classified environments [1].
Robotic cell therapy manufacturing: economic and operational gains
Industry‑based modeling in the peer‑reviewed work suggests roughly 70% lower GMP‑level manufacturing costs per product when robotic expansion replaces manual methods [1]. Additional data from the company and partners report about a 74% overall cost reduction across the broader workflow, reinforcing the potential OPEX gains when automation is applied end‑to‑end [2][3]. These savings come from:
- Higher throughput via parallelized execution across multiple robot arms [2]
- Reduced labor intensity in repetitive, time‑controlled steps [1][2]
- More efficient use of cleanroom and vertical space, including ceiling‑mounted arms [2]
Cleanroom footprint is a critical limiter for advanced therapy production. Multiply Labs’ compact clusters can deliver up to 100 times more patient doses per square foot, substantially increasing capacity without major facility expansions [2]. For programs constrained by facility scale or labor availability, these shifts can translate into faster timelines and more predictable batch economics [1][2][3].
Quality, safety, and regulatory considerations
Human operators are a primary contamination vector in cell therapy manufacturing. By removing direct touchpoints, the robotic process reduces contamination risk and has maintained sterility in non‑classified environments—evidence that supports robust quality outcomes even outside traditional cleanroom classifications [1]. Because the architecture works with existing, leading instruments and established protocols, manufacturers can limit process redesign, easing tech transfer and regulatory friction [1]. For broader regulatory context, see the FDA’s current good manufacturing practice framework (external).
A practical path to adoption
For leaders evaluating cell therapy manufacturing automation, a pragmatic route often includes:
- Pilot a focused use case like T cell expansion to validate quality equivalence and throughput gains [1]
- Map integration to existing instruments and protocols to minimize validation overhead [1]
- Quantify CAPEX/OPEX impacts, incorporating modeled ~70% GMP cost reductions and broader ~74% savings where applicable [1][2][3]
- Design facility layouts to leverage vertical stacking and ceiling‑mounted arms for space efficiency [2]
- Align operations, QA, and regulatory teams early to streamline validation and documentation [1]
Teams exploring end‑to‑end modernization can also benchmark against peers and proven platforms from robotics partners like Universal Robots, which feature prominently in these deployments [2]. For more structured frameworks, Explore AI tools and playbooks.
Limitations and what to watch next
While the results are promising, stakeholders will track long‑term validation across more sites, continued evidence on broader instrument compatibility, and additional peer‑reviewed studies confirming outcomes at scale. Given the demonstrated cost, sterility, and throughput benefits, the next wave of data will likely focus on multi‑site reproducibility and end‑to‑end automation across additional unit operations [1][2][3].
When the business case turns on
For programs facing high labor costs, limited cleanroom capacity, or contamination risk, the case for robotics‑driven biomanufacturing is compelling: peer‑reviewed quality parity, modeled ~70% GMP cost reductions, up to 100x more doses per square foot, and integration with existing tools [1][2][3]. As deployment expands, robotic cell therapy manufacturing is poised to help move advanced therapies from bespoke to scalable—and from scarce to more broadly accessible [1][2][3].
Sources
[1] Multiply Labs Unveils First Peer-Reviewed Study Showing that Robotic Cell Expansion Can Match the Performance and Reduce the Costs of a Manual Process
https://www.biospace.com/multiply-labs-unveils-first-peer-reviewed-study-showing-that-robotic-cell-expansion-can-match-the-performance-and-reduce-the-costs-of-a-manual-process
[2] Robotics transforms cell therapy: Multiply Labs slashes costs by 74%
https://www.universal-robots.com/news-and-media/news-center/robotics-transforms-cell-therapy/
[3] Multiply Labs cuts costs by 74% with UR robots – LinkedIn
https://www.linkedin.com/posts/multiply-labs_costsavings-throughput-biotech-activity-7371221182282616832-Vatv